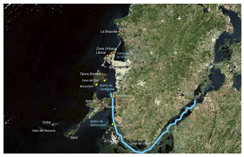
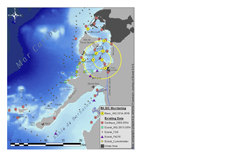
This research project is based in the coastal zone of Cartagena, Colombia. Located on the Caribbean coast in the north of Colombia, Cartagena and its surrounding beaches represent the country´s principal touristic destination. The project´s hydrological studies focus on Cartagena Bay, the Dique Canal and the Magdalena River watershed. The project´s socio-economic studies focus on the local communities in the areas surrounding Cartagena Bay, principally the communities of Ararca and Barú.
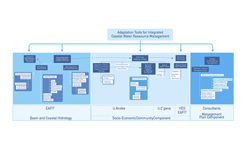
The BASIC Project`s general objective is to generate adaptation tools for integrated coastal water resource management in the coastal zone of Cartagena, towards the reduction of pollution risks, ecosystem service conservation and climate change adaptation. The hydrology component of the project will be implemented by EAFIT. The University of Los Andes will lead the project´s socio-economic component with support from the Foundation H.E.O., while the University of Cartagena will carry out studies of public health in the communities.The management plan component will be done by independent consultants.
Studies of fluvial hydrology are dedicated to research of the Magdalena River basin, with a focus on surface waters that flow from the Dique Canal towards Cartagena Bay.Analysis of the watershed´s human development and climatic conditions will permit modelling of the watershed´s runoff processes. Future scenarios of climate change and human development will be used to generate prognostics of freshwater discharge from the Dique Canal into Cartagena Bay.
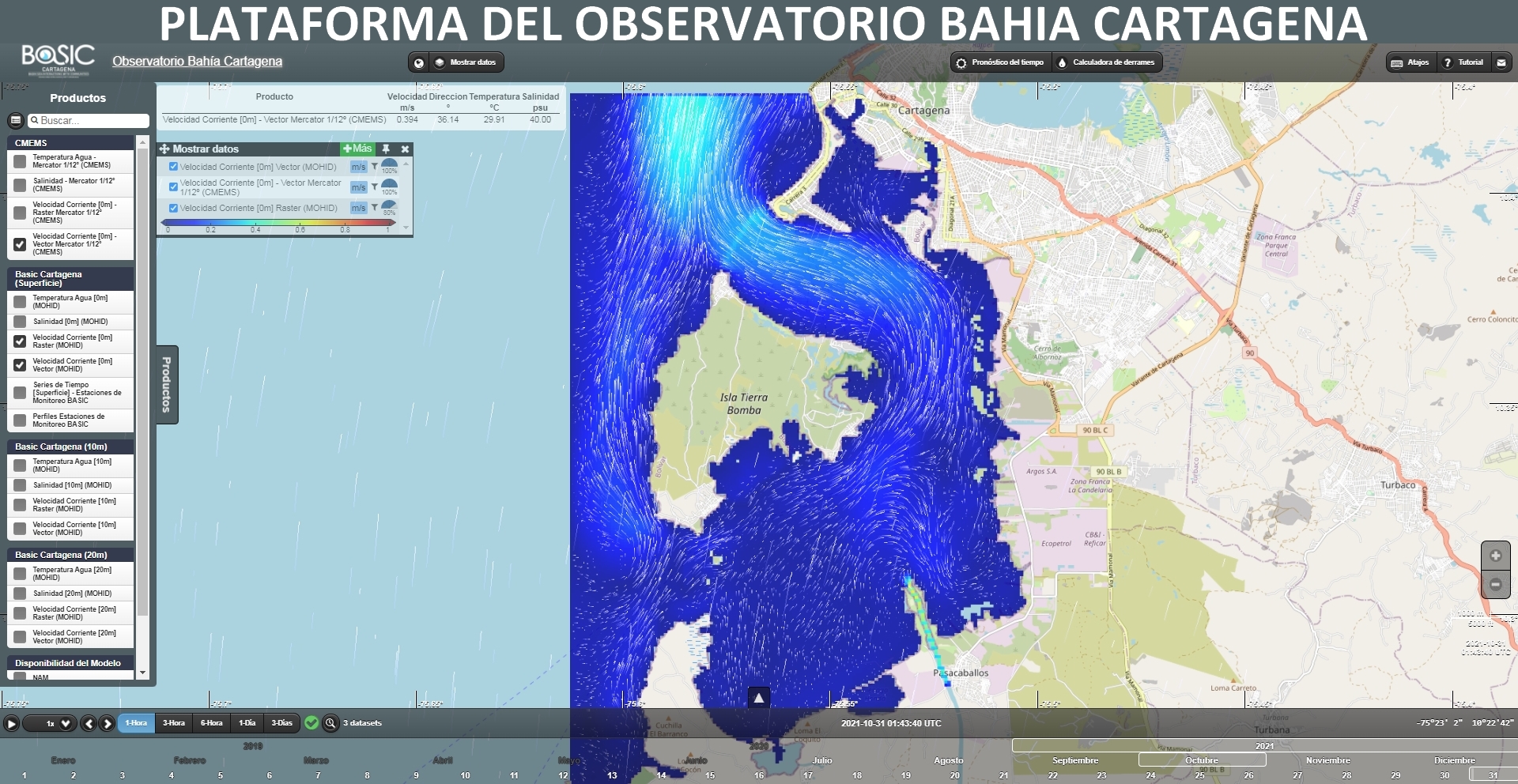
Studies of coastal hydrology focus on the monitoring of water quality and sediment in Cartagena Bay. Analysis of physico-chemical and microbiological parameters, as well as contaminants, will permit an impact assessment of human activities and climate variation on the sea, as well as the generation of vulnerability maps. Hydrodynamic modelling will be used for prognostics of the dispersion of fresh water from the Dique Canal into Cartagena Bay under future watershed scenarios.
Studies of fish ecotoxicology focus on the artisanal fisheries of local communities in the islands surrounding Cartagena. Analysis of the genetic diversity and contaminant load found in the fish will permit an assessment of the impact of pollution onartisanal fisheries. This diagnostic complements the project´s socio-economic studies and provides an appropriation of knowledge to the local communities towards the optimization of their artisanal fisheries. Some of the local fishermen will be involved in theproject, assisting to collect baseline data on the fish (weight, size) and to collect samples used for genetic and toxicological analyses.
The project´s socio-economic studies focus on artisanal fisheries and tourism, which are the main economic activities of local communities in the islands surrounding Cartagena. Analysis of the dynamics of these economic activities will permit a valuation of the potential impact that pollution could have on these communities. This work with the communities seeks to identify strategies that can alleviate potential socio-economic impacts of pollution on tourism, artisanal fisheries and public health.
The project´s research of public health focuses on health indices related to problems of water management in the local communities in the islands surrounding Cartagena. The collection of information through surveys and existent documentation permits the identification of potential risks to which the communities could be exposed. The creation of a public knowledge base on these problems in the local communities forms the first step towards mitigation of such risks.
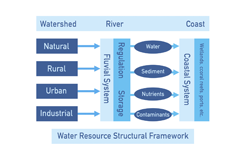
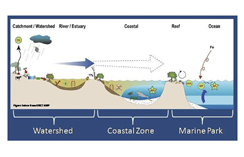
An important strategy for water protection is at the political level and the use of management plans. However, management of the coastal system is divided among different administrations which which are responsible for the watershed, the coastal zone and the marine park separately. This component of the project seeks to find strategies to align these plans towards the integrated management of the continental basin, the sea and the coastal communities.
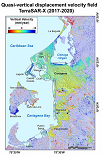
The study of relative change in sea level in Cartagena bay focuses on the collection of data from tide gauges, satellites and geodesic stations. The analysis evaluates the rate of increase or decrease of the relative sea level over the past years. This comparison makes it possible to determine what proportion of sea level rise is attributed to global warming and subsidence of the land. This research component has been implemented by EAFIT University in collaboration with the GeoRED Project of the Colombian Geological Service.
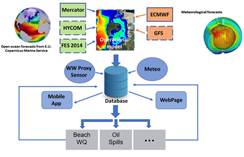
The project aims to develop an early warning system (EWS) to forecast events and trends of pollution in Cartagena Bay. BASIC is building a real-time EWS with a focus on two significant problems in the bay: 1) sanitary contamination of recreational waters of tourist beaches, and 2) spill events. For this reason, BASIC has joined forces with several partners for the development of the system, including the University of Algarve (Portugal), the Naval School Admiral Padilla (ENAP) of Cartagena, and CEGEP-St. Laurent (Canada). The final product of the system will include interactive platforms and mobile applications, and will be aimed at the CARDIQUE Corporation and CIOH-DIMAR as end users and authorities of the bay.
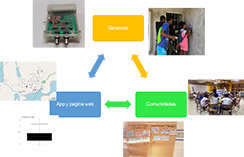
BASIC works with the coastal communities of Cartagena in activities of drinking water monitoring, community capacity building and the design of water systems. In the community of Barú, the project is developing designs and prospecting for an aqueduct and possible viable systems for wastewater treatment. A community water quality monitoring system is also being constructed with the technological development of low-cost sensors and the generation of information on the use of water resources in the communities. BASIC also offers medical support to all coastal communities, including the diagnosis of drinking water and interventions of educational capacity building in the communities.
This component aims to develop a community-based monitoring system for assessing
drinking water quality in rural communities in the coastal area of Cartagena Bay.
The idea behind this is that citizens can have access to information regarding the
quality of water they consume at home in these communities with limited access to
drinking water. The basis of the system is the interaction between technology and
society. In particular, the combination of hardware, software, and communities to
ensure the system’s sustainability. To do so, BASIC is conducting a series of activities
and developing products in these three aspects: 1) construction of low-cost sensors
(SensoAgua v4) for assessing water quality parameters such as dissolved oxygen,
temperature, conductivity, and pH; 2) development of an app to collect data through
cellphones (Calprobe) and an interface to store and visualize the results; and 3) the
design of strategies for community appropriation using experimental games to analyze
the motivation in communities to produce public information on water quality and its
importance for public health purposes. For more information, see:
https://monitoreociudadano.uniandes.edu.co
Copyright © 2014-2017 BASIC Cartagena: Interacciones entre Cuencas, Mar y Comunidades – Basin Sea Interactions with
Communities. Universidad EAFIT, Carrera 49 N° 7 Sur - 50, Medellín, Colombia.